Comparing Models
The Model Comparison page allows you to dive into the detailed performance of models by enabling you to recompute metrics for data matching specific criteria (a specific geolocation, time of day, sensor type, etc.). It also provides examples of where the model made mistakes and where it was correct.
Setting Up Model Comparisons
First, on the left-hand side, select up to six models and a dataset to create a comparison set. You can create multiple comparison sets if desired, but the total number of models across comparison sets is currently limited to six.
Click Calculate Metrics. For large datasets, you may need to wait a couple of minutes for all the metrics to finish processing. Once they have finished, you will see the page populate with various metrics, graphs, and examples.
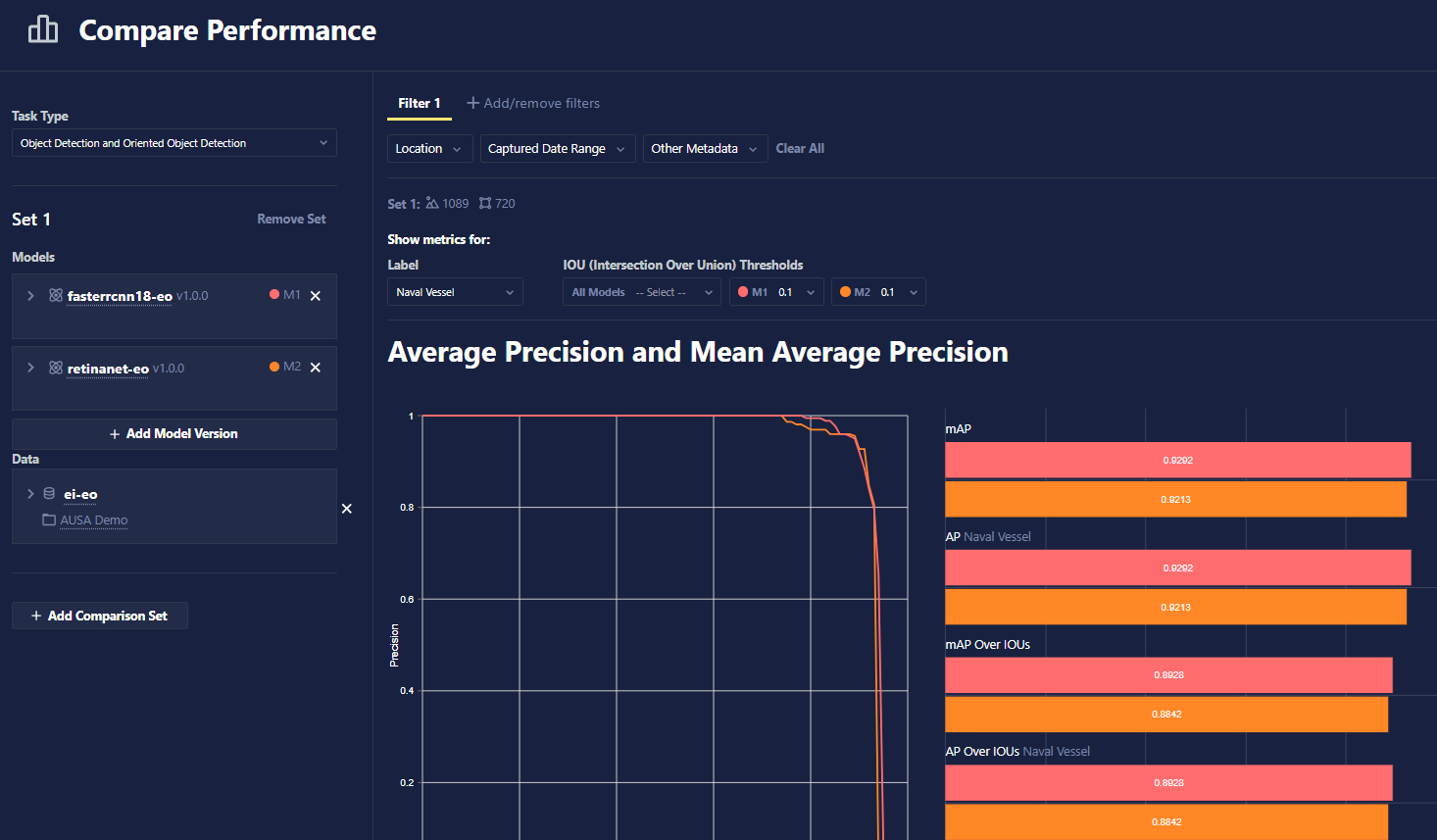
Filtering and Customization
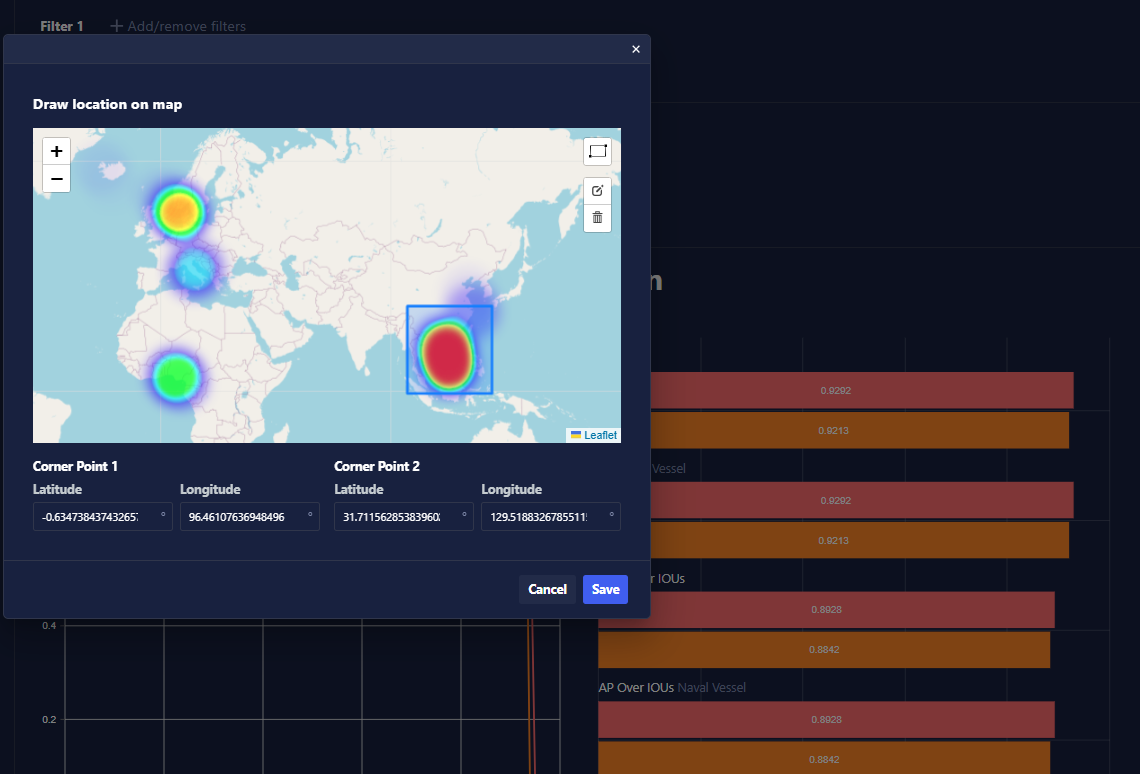
If you would like to filter metrics by class label, metadata, or location, or if you would like to adjust certain thresholds used for computing metrics, such as Intersection over Union (IoU), the metrics will be updated nearly instantaneously.
Detection Examples
For detection models, the comparison page will include examples of:
- Unmatched predictions: An instance where there was a prediction but no ground truth annotation in the region; this is often referred to as a false positive.
- Unmatched ground truths: An instance where there was a ground truth annotation but the model made no prediction; this is often referred to as a false negative.
- Misclassifications: The model predicted something, but it was the wrong class label.
- Accurate predictions: The model made a prediction that matches the class label and the IoU threshold; this is often referred to as a true positive.